Answer:
The answer is "$ 140".
Step-by-step explanation:
The company produces the quantity MR = MC and if there is no quantity MR = MC, the amount throughout the case MR is just greater and closest to MC to maximize profit.
Here MR = marginal income and marginal cost =MC
MR =
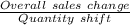
In the above table, we could see that the amount MR = MC = 8 isn't available. Thus it produces the amount where the MR
is only larger but nearest to MC.
25 unit MR =
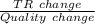
![= [TR (when \ Q = 25) -TR ((when \ Q = 20)])/((25 - 20))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/business/high-school/hk2ms5822nsmhbq60emtzczknjmnxrkmx9.png)
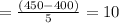
(Minimum and superior to MC)
MR of 30 units
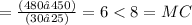 , similarly MR of 30 units.
, similarly MR of 30 units.
Consequently, 25 units were produced and 12.5 units were produced.
Currently, XYZ breaks the agreement and produces three more so thus maximum quantity produced on a market = 25 + 5 = 30 and through the above table they see which if quantity = 30, price = 16.
XYZ produces 12.5 + 5 = 17.5 output from 30 units.
Cost Total = TVC + TFC
Total TVC = Total Cost for Variable TFC = Maximum Cost of TFC = 0.
If MC is stable, TVC = MC
 Q = 8
Q = 8
 q, where Q = exposed to the real produced and XYZ produces 17.5 in this case.
q, where Q = exposed to the real produced and XYZ produces 17.5 in this case.
Total expenditure (TC+) is TVC = TFC = 8
 17.5.
17.5.
Take control = TR - TC = TC = 16
 17.5 - 8
17.5 - 8
 17.5 = 150.
17.5 = 150.
So the business XYZ is profiting = 140