Answer: The total momentum before the docking maneuver is
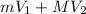 and after the docking maneuver is
and after the docking maneuver is
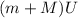
Step-by-step explanation:
Linear momentum
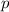 (generally just called momentum) is defined as mass in motion and is given by the following equation:
(generally just called momentum) is defined as mass in motion and is given by the following equation:
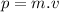
Where
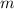 is the mass of the object and
is the mass of the object and
 its velocity.
its velocity.
According to the conservation of momentum law:
"If two objects or bodies are in a closed system and both collide, the total momentum of these two objects before the collision
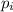 will be the same as the total momentum of these same two objects after the collision
will be the same as the total momentum of these same two objects after the collision
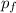 ".
".
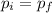
This means, that although the momentum of each object may change after the collision, the total momentum of the system does not change.
Now, the docking of a space vehicle with the space station is an inelastic collision, which means both objects remain together after the collision.
Hence, the initial momentum is:
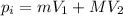
Where:
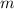 is the mass of the vehicle
is the mass of the vehicle
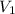 is the velocity of th vehicle
is the velocity of th vehicle
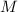 is the mass of the space station
is the mass of the space station
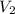 is the velocity of the space station
is the velocity of the space station
And the final momentum is:
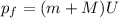
Where:
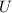 is the velocity of the vehicle and space station docked
is the velocity of the vehicle and space station docked