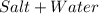(A) Water
Neutralization, the chemical reaction combining an acid with a base to produce a neutral solution, produces a salt and water.
Step-by-step explanation:
Neutralization is a double displacement chemical reaction where an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water. The reaction only products neutral compounds and is reversible in nature.
Based on Arrhenius' acid and base theory, an acid when dissolved in water produces positive hydrogen (
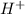 ) ion and negative non-metal ions. A base when dissolved in water produces positive metal ions and negative hydroxide (
) ion and negative non-metal ions. A base when dissolved in water produces positive metal ions and negative hydroxide (
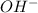 ) ions. When an acid reacts with a base, the hydrogen ions react with the hydroxide ions to form water.
) ions. When an acid reacts with a base, the hydrogen ions react with the hydroxide ions to form water.
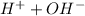 →
→
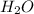
The metal and non-metal ions combine to form a neutral ionic compound, the salt.
Eg: Combination of Sodium Hydroxide (
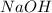 ) and hydrochloric acid (
) and hydrochloric acid (
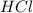 ) forms Water (
) forms Water (
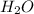 ) and Common salt (
) and Common salt (
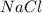 )
)
Equation:
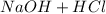 ⇄
⇄
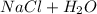
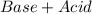 ⇄
⇄