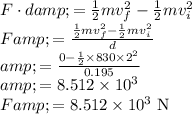Answer:
8512 N
Step-by-step explanation:
From the work energy theorem we know that: The net work done on a particle equals the change in the particles kinetic energy:
![W=\Delta K=K_(f)-K_(i) \\ \\qquad \begin{array}{r} W=F \cdot d, \Delta K=(1)/(2) m v_(f)^(2)-(1)/(2) m v_(i)^(2) \\ F \cdot d=(1)/(2) m v_(f)^(2)-(1)/(2) m v_(i)^(2)]()
Where:
-W is the work done by the force.
- F is the force actin on the.
- d is the distance travelled.
- m is the mass of the car.
-
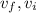 are the final and the initial velocity of the car
are the final and the initial velocity of the car
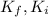 are the final and the kinetic energy of the car.
are the final and the kinetic energy of the car.
Givens:
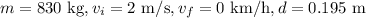
Plugging known information to get: