Answer:

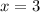
Explanation:
Given:
![g(x)=\sqrt[3]{(x+3)/(4)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/qcmkoz24k3g149g14ckor8jkciu3ddce2s.png)
To find the value of x such that g(2x) = (g(x))², substitute x = 2x into g(x), then equate it to the square of function g(x):
![\begin{aligned}g(2x)&=(g(x))^2\\\\\sqrt[3]{(2x+3)/(4)}&=\left(\sqrt[3]{(x+3)/(4)}\right)^2\end{aligned}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/5dh4og6hseqldrkbr9ka3k1emfcx4gqi2d.png)
![\textsf{Apply the exponent rule:} \quad \left(\sqrt[n]{a}\right)^m=a^{(m)/(n)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/college/ogh519yjqyy8hcqlitq6f0prbxxps2bbx0.png)
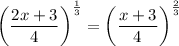
Cube both sides of the equation:
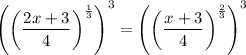
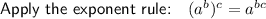
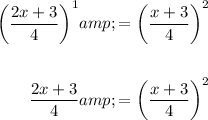

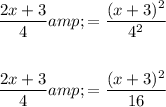
Cross multiply and expand:
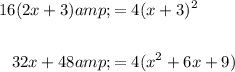
Divide both sides by 4:
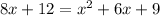
Rearrange to ax² + bx + c = 0 form:
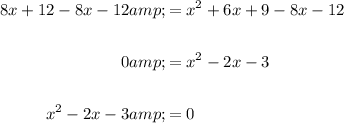
Factor and solve for x:
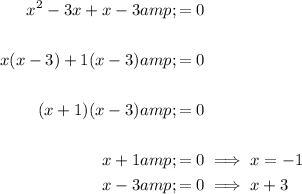
Therefore, the two values of x are x = -1 and x = 3.