Final answer:
The value of c^2(\delta t')^2 - (\delta x')^2 in the context of special relativity, using Lorentz transformations, simplifies to the invariant interval (\delta t)^2c^2 - (\delta x)^2 after canceling out the velocity-dependent terms.
Step-by-step explanation:
The question is asking to find the value of c^2(\delta t')^2-(\delta x')^2 in the context of special relativity, where \gamma is the Lorentz factor, \delta x is the spatial interval, \delta t is the time interval, and c is the speed of light.
According to the Lorentz transformation, the relationship between time intervals \delta t and \delta t', and space intervals \delta x and \delta x' in different inertial reference frames is given by:
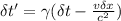
and
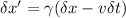
Squaring these expressions and subtracting (\delta x')^2 from c^2(\delta t')^2, we get:
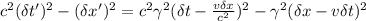
Expanding and simplifying, we use the identity \gamma^2 = 1/(1 - (v/c)^2) and note that terms involving v\delta x and v\delta t will cancel out, resulting in:
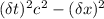
Therefore, the value of
