Solution :
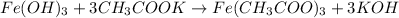
(iron (potassium
hydroxide) acetate)
Number of moles of
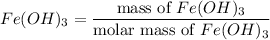
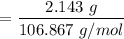
= 0.02005 mol
Number of moles of
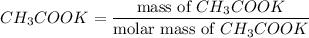
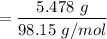
= 0.0585 mol
Since 1 mol of
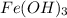 reacts with 3 mols of
reacts with 3 mols of
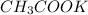
Therefore, number of moles of
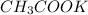 reacted
reacted
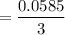 mol
mol
= 0.0195 mol
Therefore the limiting reagent is
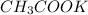 and hence the number of moles of
and hence the number of moles of
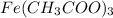 produced is 0.0195 mol
produced is 0.0195 mol
Amount of
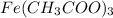 produced = moles x molar mass
produced = moles x molar mass
= 0.0195 moles x 232.98 g/mol
= 4.5431 g