Answer:
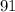
Explanation:
The partial sum of a sequence is the sum of a certain number of terms in the sequence. For the given sequence
{0, −1, −3, −6, −10, ...},
The nth term can be represented as Tn = n(n-1)/2. This means that the partial sum of the first 14 terms of the sequence, denoted by S14, can be calculated by adding up the first 14 terms using the formula: S14 = 0 + (-1) + (-3) + (-6) + (-10) + ... + T14.
Simplifying this expression using the formula for Tn, We get S14 = 91. Therefore, the partial sum for the given sequence up to the 14th term is equal to 91.