Answer: D.) SAS
Explanation:
SAS congruence postulate says that if two sides and the included angle of a triangle are congruent to corresponding two sides and the included angle of other triangle then we say the two triangles are congruent.
In the given proof , in ΔABD and ΔACD
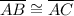 [side] (given)
[side] (given)
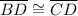 [side] (given)
[side] (given)
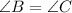 [included angle] (Base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent.)
[included angle] (Base angles of isosceles triangles are congruent.)
So by SAS congruence postulate ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.