This is an example of transformation of a parent function. If you know the graph of the parent function, you just need to know how the transformation affect its shape, and you can graph any function derived from the parent one.
In this case, the parent function is
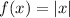 , i.e. the classic V-shaped function, with its spike on the origin. Now, about the transformation:
, i.e. the classic V-shaped function, with its spike on the origin. Now, about the transformation:
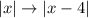
is a transformation of this kind:
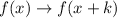 . These transformations result in horizontal translations,
. These transformations result in horizontal translations,
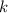 units to the left if
units to the left if
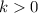 , to the right if
, to the right if
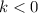 . So, in your case, the graph if shifted to the right by 4 units.
. So, in your case, the graph if shifted to the right by 4 units.
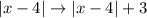
is a transformation of this kind:
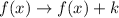 . These transformations result in vertical translations,
. These transformations result in vertical translations,
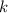 units down if
units down if
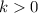 , up if
, up if
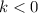 . So, in your case, the graph if shifted upwards by 3 units.
. So, in your case, the graph if shifted upwards by 3 units.
So, in the end, if you start from the graph of
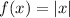 , you can plot the graph of
, you can plot the graph of
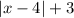 by shifting the parent function 4 units to the right and 3 units up.
by shifting the parent function 4 units to the right and 3 units up.