Answer:- Equilibrium partial pressure of
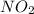 is 1.05 atm.
is 1.05 atm.
Solution:- The given balanced equation is:
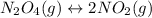
Equilibrium expression for the equation is written as:
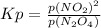
(In this expression p stands for partial pressure.)
If we consider the initial partial pressure for the reactant gas as m and the product gas as 0 since initially there is no product. Let's say the change in pressure is n. Then equilibrium partial pressure of reactant gas will be (m-n) and reactant gas equilibrium partial pressure be 2n since it's coefficient is two.
Equilibrium partial pressure of reactant gas is given as 3.48 atm. It means (m-n) = 3.48
Let's plug in the values in the equilibrium expression:
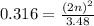
On cross multiply:
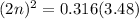
Taking square root to both sides:
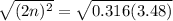
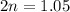
So, the equilibrium partial pressure of
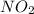 is 1.05 atm.
is 1.05 atm.