Answer:
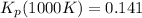
Step-by-step explanation:
From the reaction:
C₂H₆(g) ⇆ C₂H₄(g) + H₂(g)
48% 26% 26%
Knowing the composition of the mixture at equilibrium (at 1000K), we can calculate the equilibrium constant in terms of mole fraction:
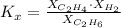
where X: mole fraction of C₂H₆(g), C₂H₄(g) and H₂(g)
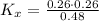
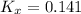
Now, the equilibrium constant in terms of pressure can be calculated using the equilibrium constant in terms of mole fraction:
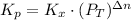
where
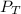 : total pressure and Δn: number of gaseous moles of product - number of gaseous moles of reactant
: total pressure and Δn: number of gaseous moles of product - number of gaseous moles of reactant
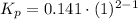
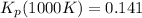
Have a nice day!