Answer:
0.1132 kJ/K the total heat capacity of the calorimeter.
Step-by-step explanation:
The combustion energy of glucose = 15.57 kJ/g.
Energy released on 2 combustion of 2.000 g of glucose = Q

Q=31.140 kJ
Heat gained by the calorimeter = Q'
Heat gained by the calorimeter = heat released on combustion of glucose
Q'= 31.140 kJ
Temperature change of the calorimeter = ΔT = 23.34°C - 21.45°C = 1.89°C
ΔT = 1.89°C = 275.04 K
Total heat capacity of the calorimeter = C
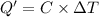

0.1132 kJ/K the total heat capacity of the calorimeter.