Answer : The work done is, 25 J
Step-by-step explanation :
As we know that work is the difference between the final and initial kinetic energy.
That means,
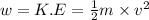
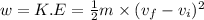
where,
w = work done
m = mass = 2 kg
K.E = kinetic energy
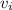 = initial speed = 0 m/s
= initial speed = 0 m/s
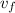 = final speed = 5 m/s
= final speed = 5 m/s
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:

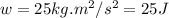
Therefore, the work done is, 25 J