Answer:
specific volume = 1.025 m³/kg
Step-by-step explanation:
given data
total mass m1 +m2 = 80 kg
specific volume = 0.8 m³/kg
occupies volume v1 = 40 m³
other gas specific volume = 1.4 m³
to find out
How much volume is occupied by the second gas and what is the specific volume of the mixture
solution
we know that density is reciprocal of specific volume and here gas is not interacting
so total specific volume is assume so ratio is total volume to total mass
and
specific volume =

here ρ is density
so ρ1 =
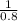 = 1.25 kg/m³
= 1.25 kg/m³
and ρ2 =
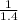 = 0.714 kg/m³
= 0.714 kg/m³
and
so m1 = ρ1v1 = 1.25 × 40 = 50 kg
and m2 = 80 - 50 = 30 kg
so
v2 =
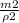
v2 =
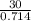 = 42 m³
= 42 m³
so volume occupied by second das = 42 m³
and
specific volume of mixture will be
specific volume of mixture =
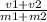
specific volume =
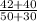
specific volume = 1.025 m³/kg