Answer with Explanation:
The force that is exerted on a object is proportional to the rate of change of momentum. Mathematically
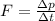
As we can see from the above equation the force that is exerted on the object is inversely proportional to the time in which this momentum change is brought meaning if the time interval in which the momentum change is brought about is larger smaller the force that acts on the object.
When the driver of a car crashes into a barrier the airbags in the car are deployed instantly as due to inertia of motion the driver continues to move in the original direction of motion thus hitting the air bag in the process. Since the air in the airbag is compressible it increases the time in which this momentum becomes zero, reducing the force that is exerted on the person, thus protecting the person.