Answer:
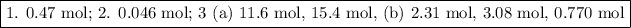
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Moles of Na
(a) Balanced equation
2Na + 2H₂O ⟶ 2NaOH + H₂
(b) Calculation
You want to convert moles of H₂ to moles of Na
The molar ratio is 2 mol Na:1 mol H₂
Moles of Na = 4.0 mol H₂ × (2 mol Na/1 mol H₂) = 8.0 mol Na
You need
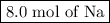 to form 4.0 mol of H₂.
to form 4.0 mol of H₂.
2. Moles of LiCl
(a) Balanced equation
2LiBr + Cl₂⟶ 2LiCl + Br₂
(b) Calculation
You want to convert moles of LiBr to moles of LiCl
The molar ratio is 2 mol LiBr:2 mol LiCl
Moles of LiCl = 0.046 mol LiBr × (2 mol LiCl/2 mol LiBr) = 0.046 mol LiCl
The reaction will produce
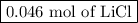 .
.
3. Combustion of propane
C₃H₈ +5O₂ ⟶ 3CO₂ +4H₂O
(a) Moles of CO₂ and H₂O
Moles of CO₂ = 0.647 mol O₂ × (3 mol CO₂/1 mol C₃H₈) = 11.6 mol CO₂
Moles of H₂O = 3.85 mol O₂ × (4 mol CO₂/1 mol C₃H₈) = 15.4 mol H₂O
The reaction produces
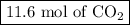 and
and
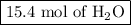 .
.
(b) Moles from O₂
Moles of CO₂ = 3.85 mol O₂ × (3 mol CO₂/5 mol O₂) = 2.31 mol CO₂
Moles of H₂O = 3.85 mol O₂ × (4 mol CO₂/5 mol O₂) = 3.08 mol H₂O
Moles of C₃H₈ = 3.85 mol O₂ × (1 mol C₃H₈/5 mol O₂) = 0.770 mol C₃H₈
The reaction produces
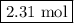 of CO₂,
of CO₂,
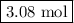 of H₂O, and consumes
of H₂O, and consumes
 of C₃H₈.
of C₃H₈.