Answer:
The resistance is decreasing at a rate of 0.36 ohms/minute.
Explanation:
The mathematical form of the Ohm's law is given by :
V = IR ...(1)
Where V is voltage, I is current and R is resistance
Given,
I = 5 A
R = 6 ohms
dI/dt = 0.3 A/min
Differentiate equation (1) wrt t:
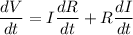
When V is constant, dV/dt = 0
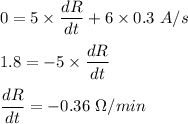
So, the resistance is decreasing at a rate of 0.36 ohms/minute.