Answer:
S = 0.10253 kW/k
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
Velocity of oxygen ( V ) = 70 m/s
Diameter of pipe = 12-cm = 0.12 m
At entrance
pressure of oxygen ( p1 ) = 240 kPa
Temperature of oxygen ( T1 ) = 20°c = 293 k
At exit
pressure of oxygen ( p2 ) = 200 kPa
temperature of oxygen ( T2 ) = 18°c = 291 k
First calculate specific volume of oxygen at inlet
V1 =
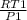 -------- ( 1 )
-------- ( 1 )
R = 0.2598 KJ/kgk ( property of oxygen )
T1 = 293 k
P1 = 240 kpa
substitute values into equation 1
V1 = 0.3172 m^3/kg
next we calculate the mass flow rate of Oxygen
m =
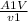 ----- ( 2 )
----- ( 2 )
A1 ( area of pipe ) = 0.0113 m^2 ( calculated )
V = 70 m/s
V1 = 0.3172 m^3/kg
substitute value into equation 2
m ( mass flow rate of oxygen ) = 2.4936 kg/s
Finally calculate the rate at which entropy is generated in the pipe
S =
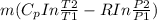 --------- ( 3 )
--------- ( 3 )
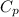 = 0.918 kj/kgk ( property of oxygen )
= 0.918 kj/kgk ( property of oxygen )
T2 = 291 k
T1 = 293 k
P2 = 200 kPa
P1 = 240 kPa
substitute values into equation 3 above
S = 0.10253 kW/k