Answer:
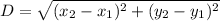
Explanation:
The distance between two points A(x₁,y₁) B(x₂,y₂) is given by the formula as follows :
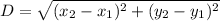
It is used to find the distance between two points. It is an application of the Pythagorean theorem. Usually, the distance covered is equal to the product of speed and time. But when speed and time in not given but coordinates are given, then only we can use this formula.