Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
The brain cell which uses glucose transporter GLUT3 Km = 1.5 mM
The liver cell which stores glucose GLUT2 Km = 15 mM
The objective is to calculate the rate (as % of Vmax) of glucose uptake in brain cells and liver cells under starvation conditions.
Using the M-M equation i.e Michaelis- Menten equation;
![Rate = (V_(max)* [S])/([S]+K_m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/9b3rbkp9kqqzm1pl5lx6tdwxrqhgx0w273.png)
By rearrangement
![(Rate)/(V_(max))= ([S])/([S]+K_m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/7irvsanq5jbyrixfano7nz0z0rhlqrajy9.png)
where;
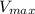 = maximum velocity of a reaction
= maximum velocity of a reaction
Thus; the rate as a % of Vmax of glucose uptake in brain cells is calculated as:
![(Rate)/(V_(max))= ([3 \ mM])/([3 \ mM]+1.5 \ mM)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/5ljqi8kezcy9ay56i9ld8ulcdw2536cras.png)
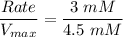
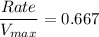
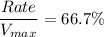
the rate as a % of Vmax of glucose uptake in liver cells is calculated as:
![(Rate)/(V_(max))= ([3 \ mM])/([3 \ mM]+15 \ mM)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/biology/college/hxrkqoez4ljq824xoakd8izljofvxxkzw5.png)
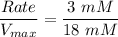
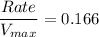
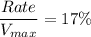
Thus, the uptake is larger brain cells due to the fact that the brain cells GLUT3 have higher tendency to attract glucose.