Answer:
The quantity of heat necessary to change the temperature of 3.00 mol of the substance from 27°C to 227°C is 19.668 KJ
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question, The empirical equation is
C=29.5J/(mol⋅K)+(8.20×10−3J/(mol⋅K2))T
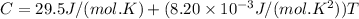
Now, to determine the heat necessary to change the temperature of 3.00 mol of this substance from 27∘C to 227∘C, that is ΔQ
From, dQ=nCdT
Integrating both sides, we get
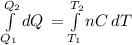
![{Q_(2)} -{Q_(1)} = \int\limits^ {T_(2) }_{T_(1) } n[ {29.5J/(mol.K)+(8.20* 10^(-3) J/(mol.K^(2) ))T} \, ]dT](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mq52vasettz15ia2rpsr1oglxwof6hd67i.png)
![\Delta Q = \int\limits^ {T_(2) }_{T_(1) } 3.00mol[ {29.5J/(mol.K)+(8.20* 10^(-3) J/(mol.K^(2) ))T} \, ]dT](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5iupk00lbi360utb4f2c08zmrwc5gjf5ci.png)
![\Delta Q = \int\limits^ {T_(2) }_{T_(1) } [ {88.5J/K+ (24.6* 10^(-3) J/K^(2) )T} \, ]dT](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/iuqm8j9feskvxyobvu7rk2gp7k7fvymkuk.png)
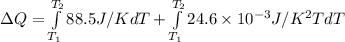
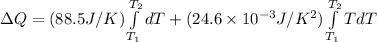
(NOTE:
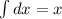 and
and
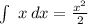 )
)
Hence, we get
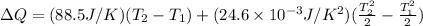
From the question,
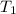 = 27 °C = (27+273) K = 300K
= 27 °C = (27+273) K = 300K
Also,
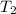 = 227 °C = (227+273) K = 500K
= 227 °C = (227+273) K = 500K
Then,
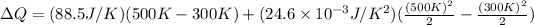
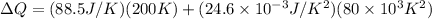
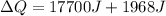
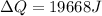
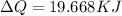
Hence, the quantity of heat necessary to change the temperature of 3.00 mol of the substance from 27°C to 227°C is 19.668 KJ
(NOTE: KJ means Kilo Joules)