Answer:
the entropy change for the surroundings when 1.62 moles of CH4(g) react at standard conditions is −8.343 J/K
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced chemical equation of the reaction in the question given is:
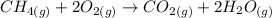
Using standard thermodynamic data at 298K.
The entropy of each compound above are listed as follows in a respective order.
Entropy of (CH4(g)) = 186.264 J/mol.K
Entropy of (O2(g)) = 205.138 J/mol.K
Entropy of (CO2(g)) = 213.74 J/mol.K
Entropy of (H2O(g)) = 188.825 J/mol.K
The change in Entropy (S) of the reaction is therefore calculated as follows:
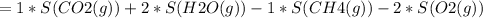
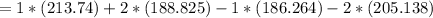
= -5.15 J/mol.K
Given that :
the number of moles = 1.62 of CH4(g) react at standard conditions.
Then;
The change in entropy of the rxn
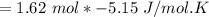
= −8.343 J/K