Answer:
a) The null and alternative hypothesis are:
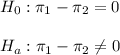
b) Yes.
Explanation:
This is a hypothesis test for the difference between proportions.
The claim is that the proportion of all NYC residents that can name a player on the Knicks differs from the proportion of all Toronto residents who can name a player on the Raptors.
As the claim is that the proportions differs, the difference to reject the null hypothesis can be positive or negative. Then, this is a two-tailed test.
The null and alternative hypothesis are:
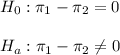
The conditions to met for this test are:
- The sampling method for each population is simple random sampling.
- The samples are independent.
- Each sample includes at least 10 successes and 10 failures.
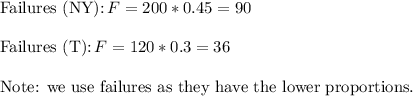
- Each population is at least 20 times as big as its sample.
This conditions are met, so all criteria for the hypothesis test is satisfied.