Answer:
-
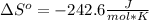
- Yes.
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, the combustion of methane is:
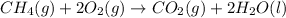
And the standard entropy of combustion is computed as:
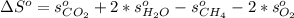
Now, looking for those data on the NIST database, we obtain:
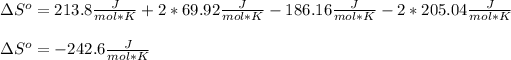
Moreover, as the result is negative, it means that the disorder decreased from reactants to products, this is noticeable by realizing that liquid water has a lower entropy than gaseous water, so YES, that also would be the sign if only the change in gaseous moles is considered.
Regards.