Answer:
Null Hypothesis,
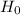 : p
: p
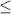 11.3%
11.3%
Alternate Hypothesis,
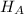 : p > 11.3%
: p > 11.3%
Explanation:
We are given that U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that 11.3% of U.S. workers belong to unions.
Suppose a sample of 400 U.S. workers is collected in 2014 to determine whether union efforts to organize have increased union membership.
Let p = % of U.S. workers belonging to union membership
So, Null Hypothesis,
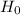 : p
: p
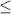 11.3%
11.3%
Alternate Hypothesis,
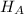 : p > 11.3%
: p > 11.3%
Here, null hypothesis states that the union membership has decreased or remained same in 2014.
On the other hand, alternate hypothesis states that the union membership has increased in 2014.
Also, The test statistics that will be used here is One-sample z proportion statistics;
T.S. =
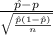 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
Hence, the above hypothesis is appropriate that can be used to determine whether union membership increased in 2014.