The pKa of the 0.25 mol sample of a weak acid calculated after its reaction with 10.0 mL of 3.00 M KOH is 4.72.
When the weak acid reacts with KOH, we have:
HA(aq) + KOH(aq) ⇄ H₂O(l) + KA(aq) (1)
The pKa of the reaction above can be calculated with the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation:
![pH = pKa + log(([KA])/([HA]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gga2p72x1hnb8sufqtsv8r0n3y0f7pckzn.png) (2)
(2)
Where:
pH = 3.85
[HA]: is the concentration of the weak acid
[KA]: is the concentration of the salt
To find the pKa, we need to calculate the values of [HA] and [KA].
First, let's find the number of moles of KOH.
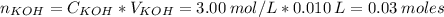
Now, when the weak acid reacts with KOH, the number of moles of the acid that remains in the solution is:
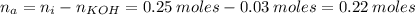
When the resulting solution is then diluted to 1.500 L, the concentration of the HA and KA is:
![[HA] = (n_(a))/(V) = (0.22\:moles)/(1.5 L) = 0.15\: mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/mnjuwygpix5oxvw35wlbn7h33vuv6xgv7b.png)
![[KA] = (0.03 \:moles)/(1.5 L) = 0.02 \:mol/L](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gc8h8c21jq3xvxv6xrgquvz6bgkrpuq0km.png)
After entering the values of pH, [HA], and [KA] into equation (2), we have:
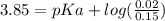
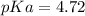
Therefore, the pKa of the weak acid is 4.72.