Answer: 5.1 gram
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the moles :
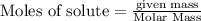
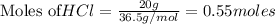
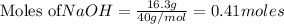
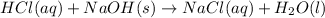
According to stoichiometry :
1 mole of
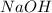 require = 1 mole of
require = 1 mole of
Thus 0.41 moles of
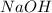 will require=
will require=
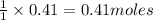 of
of
Thus
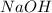 is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and
is the limiting reagent as it limits the formation of product and
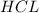 is the excess reagent.
is the excess reagent.
Moles of HCl left = (0.55-0.41) = 0.14
Mass of
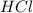 left =
left =
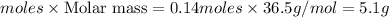
Thus 5.1 g of hydrochloric acid could be left over by the chemical reaction.