Step-by-step explanation:
Half life is the amount of time taken by a radioactive material to decay to half of its original value.
Half life for second order kinetics is given by:
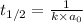
k = rate constant =?
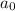 = initial concentration
= initial concentration
a = concentration left after time t
Integrated rate law for second order kinetics is given by:
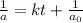
a) Initial concentration of XY =
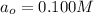
Rate constant of the reaction = k =
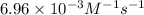
Half life of the reaction is:
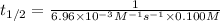
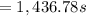
1,436.78 seconds is the half-life for this reaction.
b) Initial concentration of XY = 0.100 M
Final concentration after time t = 12.5% of 0.100 M = 0.0125 M
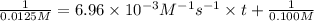
Solving for t;
t = 10,057.47 seconds
In 10,057.47 seconds the concentration of XY will become 12.5% of its initial concentration.
c) Initial concentration of XY = 0.200 M
Final concentration after time t = 12.5% of 0.200 M = 0.025 M
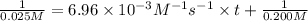
Solving for t;
t = 5,028.73 seconds
In 5,028.73 seconds the concentration of XY will become 12.5% of its initial concentration.
d) Initial concentration of XY = 0.160 M
Final concentration after time t =
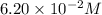
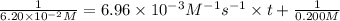
Solving for t;
t = 1,419.40 seconds
In 1,419.40 seconds the concentration of XY will become
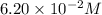 .
.
e) Initial concentration of
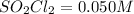
Final concentration after time t = x
t = 55.0 s
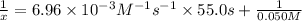
Solving for x;
x = 0.04906 M
The concentration after 55.0 seconds is 0.04906 M.
f) Initial concentration of XY= 0.050 M
Final concentration after time t = x
t = 500 s
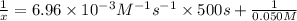
Solving for x;
x = 0.04259 M
The concentration after 500 seconds is 0.0.04259 M.