Answer:
Volume of NaOH required = 3.61 L
Step-by-step explanation:
H2SO3 is a diprotic acid i.e. it will have two dissociation constants given as follows:
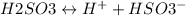 --------(1)
--------(1)
where, Ka1 = 1.5 x 10–2 or pKa1 = 1.824
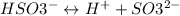 --------(2)
--------(2)
where, Ka2 = 1.0 x 10–7 or pKa2 = 7.000
The required pH = 6.247 which is beyond the first equivalence point but within the second equivalence point.
Step 1:
Based on equation(1), at the first eq point:
moles of H2SO3 = moles of NaOH
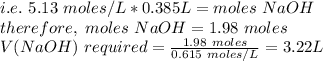
Step 2:
For the second equivalence point setup an ICE table:
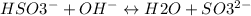
Initial 1.98 ? 0
Change -x -x x
Equil 1.98-x ?-x x
Here, ?-x =0 i.e. amount of OH- = x
Based on the Henderson buffer equation:
![pH = pKa2 + log([SO3]^(2-) )/([HSO3]^(-) ) \\6.247 = 7.00 + log(x)/((1.98-x)) \\x=0.634 moles](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/blvu5x8eadfdw2q3vd5bnubj2wimid1n1l.png)
Volume of NaOH required is:
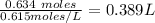
Step 3:
Total volume of NaOH required = 3.22+0.389 =3.61 L