Solution :
Given data :
Mass of ice, m = 200 g
Mass of water, M = 500 g
Temperature of ice = 0°C
Temperature of water = 20°C
We known ;
The latent heat of fusion of water is
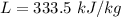
The specific heat of water, C = 4.18 kJ/kg K
a). Heat required to change the ice into water is :
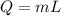
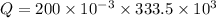
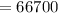 J
J
Heat required to cool the warm water is :
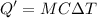
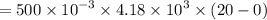
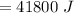
From above result,
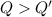
This means that total ice could not melt.
So, the temperature must be T = 0°C
b). Q' = mL
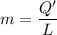
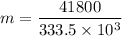
m = 0.1253 kg
m = 125.3 g
m = 125 g
Therefore, 125 g of ice had melted.