Answer:
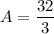
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Integrals
- Definite Integrals
- Area under the curve
Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
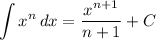
Integration Rule [Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 1]:
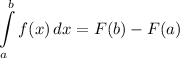
Integration Property [Multiplied Constant]:
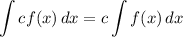
Integration Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle \int {[f(x) \pm g(x)]} \, dx = \int {f(x)} \, dx \pm \int {g(x)} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/r5yh324r81plt97j3zrr5qi2xxczxlqi34.png)
Area of a Region Formula:
![\displaystyle A = \int\limits^b_a {[f(x) - g(x)]} \, dx](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/uij08sp4x97gp23utcdwranet4linkrd6u.png)
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
Curve: x³ + 2x² - 3x
Interval: [-3, 1]
Step 2: Find Area
- Set up:
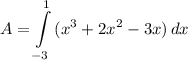
- [Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Addition/Subtraction]:
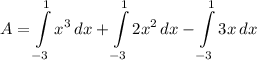
- [Integrals] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
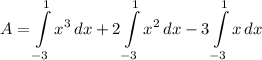
- [Integrals] Integrate [Integration Rule - Reverse Power Rule]:
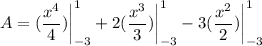
- Evaluate [Integration Rule - Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 1]:
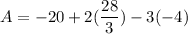
- Evaluate:
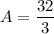
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Integration
Book: College Calculus 10e