The balanced formula of the reaction described is:
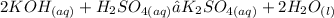
To find the molar concentration (Molarity) of the solution we will follow the following steps:
1. We find the moles of KOH present in the basic solution using the molarity equation that tells us:
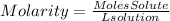
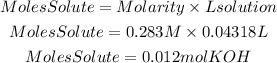
2. From the stoichiometry of the reaction we find the moles of H2SO4 needed to neutralize the moles of KOH. The ratio H2SO4 to KOH is 1/2.
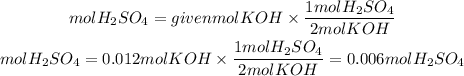
3. We find the molarity of the solution using the molarity formulation from point 1.
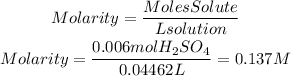
Answer: The molarity or molar concentration of the acid solution is 0.137M