The function is given to be:
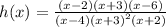
Vertical Asymptotes:
The vertical asymptote of a function is the x value gotten when the denominator is equated to 0.
The denominator of the function given can be equated to 0 as shown below:
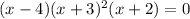
Therefore, we can get the values for x using the Zero Factor Principle given to be:
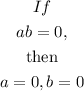
Therefore, we have
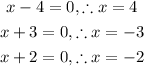
Hence, the horizontal asymptotes are at:
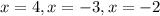
Horizontal Asymptotes:
The horizontal asymptotes can be gotten by checking the degree of the functions that make up the numerator and denominator of the whole function. If the degree of the numerator is less than that of the denominator, then the asymptote is at y = 0.
Degree of Numerator: 3
Degree of Denominator: 4
Therefore, the horizontal asymptote is at:
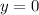
ANSWER:
The correct option is OPTION B.