Answer:
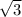 , assuming that the air resistance (drag) on the ball is negligible.
, assuming that the air resistance (drag) on the ball is negligible.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let
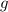 denote the gravitational field strength (
denote the gravitational field strength (
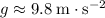 near the surface of the earth.) If the drag on the ball is negligible, the ball will be constantly accelerating downward at
near the surface of the earth.) If the drag on the ball is negligible, the ball will be constantly accelerating downward at
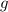 while in the air.
while in the air.
Let
 denote the initial velocity of this ball. In this example,
denote the initial velocity of this ball. In this example,
 will be the velocity at which the ball is tossed upwards.
will be the velocity at which the ball is tossed upwards.
When the ball is at maximum height, its velocity will be
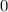 . Let
. Let
 denote this velocity.
denote this velocity.
Let
 denote the displacement of this ball when it reached maximum height relative to when the ball was initially tossed upward. In this example,
denote the displacement of this ball when it reached maximum height relative to when the ball was initially tossed upward. In this example,
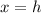 .
.
Let
 denote the acceleration of this ball. Under the assumptions,
denote the acceleration of this ball. Under the assumptions,
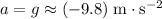 .
.
The SUVAT equation
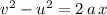 relates these quantities.
relates these quantities.
Note that since
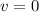 ,
,
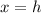 , and
, and
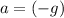 , this equation becomes:
, this equation becomes:
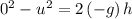 .
.
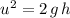 .
.
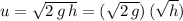 .
.
Therefore, replacing
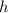 with
with
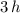 will only increase the initial velocity of the ball
will only increase the initial velocity of the ball
 by a factor of
by a factor of
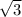 .
.