To determine pKb for the weak base, first calculate the pOH using the given pH. Then calculate the hydroxide ion concentration [
 ], followed by the base dissociation constant (Kb). Finally, take the negative logarithm of Kb to find pKb.
], followed by the base dissociation constant (Kb). Finally, take the negative logarithm of Kb to find pKb.
To determine pKb for the weak base, we can first calculate the pOH using the given pH. The pOH is found by taking the negative logarithm of the hydroxide ion concentration, and then subtracting this value from 14 to get the pH. In this case,
the pOH is 14 - 11.25 = 2.75.
Next, we can use the pOH value to calculate the hydroxide ion concentration, [
 ]. Since pOH = -log [
]. Since pOH = -log [
 ], we can rearrange the equation to find [
], we can rearrange the equation to find [
 ].
].
Taking the antilog of -2.75, we get [
 ] =
] =
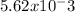 M
M
Finally, we can use the hydroxide ion concentration to calculate the base dissociation constant (Kb) using the equation Kb =
![[OH^(-) ]^2 / [base]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/p88jw5acxbbo73fjphy9v0bgwevq3r2d0k.png) values, we have
values, we have
Kb =
 =
=
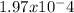
To find pKb, we can take the negative logarithm of Kb, giving us pKb = -
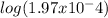 = 3.71.
= 3.71.