NaCl is stable because sodium loses one electron to form the
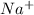 cation, while chlorine gains one electron to form the
cation, while chlorine gains one electron to form the
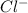 anion. On the other hand,
anion. On the other hand,
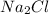 and
and
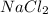 are not stable because the ratios of cations to anions are incorrect. In the case of MgO, magnesium (Mg) loses two electrons to form the
are not stable because the ratios of cations to anions are incorrect. In the case of MgO, magnesium (Mg) loses two electrons to form the
 cation, while oxygen (O) gains two electrons to form the
cation, while oxygen (O) gains two electrons to form the
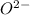 anion.
anion.
An ionic compound is formed in three steps: removing an electron from the metal, adding an electron to the nonmetal, and allowing the metal cation and nonmetal anion to come together. NaCl is stable because sodium (Na) loses one electron to form the cation,
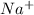 , while chlorine (Cl) gains one electron to form the
, while chlorine (Cl) gains one electron to form the
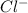 anion. The electrostatic attraction between the
anion. The electrostatic attraction between the
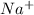 and
and
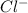 ions makes NaCl stable.
ions makes NaCl stable.
In
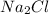 , there are two sodium ions (
, there are two sodium ions (
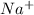 ) for every one chloride ion (
) for every one chloride ion (
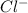 ), which results in an unstable ratio. Similarly,
), which results in an unstable ratio. Similarly,
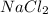 has one sodium ion (
has one sodium ion (
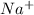 ) for every two chloride ions (
) for every two chloride ions (
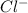 ), which also creates an unstable ratio.
), which also creates an unstable ratio.
In the case of MgO, magnesium (Mg) loses two electrons to form the
 cation, while oxygen (O) gains two electrons to form the
cation, while oxygen (O) gains two electrons to form the
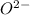 anion. The resulting compound, MgO, is stable because of the electrostatic attraction between the
anion. The resulting compound, MgO, is stable because of the electrostatic attraction between the
 and
and
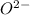 ions.
ions.
However,
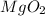 and
and
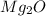 are not stable due to incorrect cation to anion ratios.
are not stable due to incorrect cation to anion ratios.
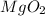 has one magnesium ion (
has one magnesium ion (
 ) for every two oxygen ions (
) for every two oxygen ions (
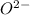 ), creating an unstable ratio.
), creating an unstable ratio.
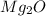 has two magnesium ions (
has two magnesium ions (
 ) for every one oxygen ion (
) for every one oxygen ion (
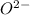 ), also resulting in an unstable ratio.
), also resulting in an unstable ratio.