The volume of 15 moles of CO₂ at 50°C and 800 torr is approximately
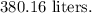
To find the volume of a gas, use the ideal gas law formula: PV = nRT, where:
- P = pressure in atm
- V = volume in liters
- n = number of moles
- R = ideal gas constant
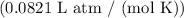
- T = temperature in Kelvin
Given:
n = 15 moles
T =
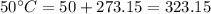 K (temperature in Kelvin)
K (temperature in Kelvin)
P = 800 torr (pressure)
Convert pressure to atm:

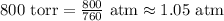
Now, rearrange the ideal gas law to solve for volume (V):
![\[PV = nRT\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/2f0lhxdptv7h7xgo1yhis0h71duuo5b3rc.png)
![\[V = (nRT)/(P)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/erf3vwt6erxlsqtmg8slmrj1rjtptwg5sz.png)
Substitute the given values:
![\[V = \frac{15 \text{ mol} * 0.0821 \text{ L atm/mol K} * 323.15 \text{ K}}{1.05 \text{ atm}}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/gr63tuk403b28fkmcbmfqfh7f5gt4as2v1.png)
Calculate the volume:
![\[V \approx (399.17225)/(1.05) \approx 380.16 \text{ L}\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/dtec50b3c0ygicg4bijcbj0b6o253qdqw4.png)