(a) The solution
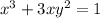 satisfies the differential equation
satisfies the differential equation
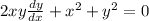 on the interval
on the interval
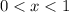 .
.
(b) The solution
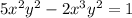 holds as an implicit solution for
holds as an implicit solution for
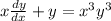 on the interval
on the interval
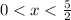 .
.
(a) Given the differential equation
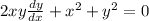 and the implicit solution
and the implicit solution
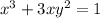 , we need to show that this solution satisfies the differential equation.
, we need to show that this solution satisfies the differential equation.
Differentiate the implicit solution
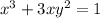 with respect to x using implicit differentiation:
with respect to x using implicit differentiation:
![\[3x^2 + 3y^2 (dx)/(dx) + 3x(dy)/(dx)2y = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/vs5l8rgk93xhu5obdc5cg4vhdk6fy5dkbw.png)
![\[3x^2 + 3y^2 + 3x(dy)/(dx)2y = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/osza5az6qvtk2zqglotl8ftmpe66qew67p.png)
![\[3x^2 + 3y^2 + 6xy(dy)/(dx) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/p3gn3l0kgqqhxpiiy5lx9yyrfk2klsqhwu.png)
![\[3(x^2 + y^2) + 6xy(dy)/(dx) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ziqby6rx9nxk2urhvoof4qwhwdyzzi0xet.png)
We know that
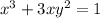 , which implies
, which implies
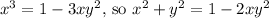 .
.
Substitute this into the differentiated expression:
![\[3(1 - 2xy^2) + 6xy(dy)/(dx) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/29v6oo3yt3jvk1vgov0qanosni4hmwuuio.png)
![\[3 - 6xy^2 + 6xy(dy)/(dx) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/hkoa8onhy9sedt64asfaqwgf7srdi51xxi.png)
![\[6xy(dy)/(dx) = 6xy^2 - 3\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/95cwgbjaq4xk2oewpjb6e5p02t34h4uxvz.png)
![\[2xy(dy)/(dx) = xy^2 - (1)/(2)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/b858fqy0fkhkei4xoi9snw0vnsrio9mjgh.png)
Now, we'll show that
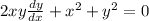 holds using the relationship
holds using the relationship
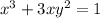 :
:
![\[2xy(dy)/(dx) + x^2 + y^2 = xy^2 - (1)/(2) + 1 - 2xy^2 = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/3lxyn88a13o5qh3zh5ydkhboskfnti9ynl.png)
![\[2xy(dy)/(dx) + x^2 + y^2 = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/aq14ugqnl4f2ujoyu1etz06k6o1oo3gycg.png)
Hence, the implicit solution
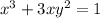 is indeed a solution of the differential equation
is indeed a solution of the differential equation
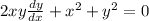 on the interval 0 < x < 1.
on the interval 0 < x < 1.
(b) For the differential equation
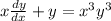 and the implicit solution
and the implicit solution
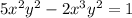 , let's verify if it holds.
, let's verify if it holds.
Differentiate the implicit solution
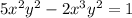 with respect to x using implicit differentiation:
with respect to x using implicit differentiation:
![\[10xy^2 + 10x^2y(dy)/(dx) - 6x^2y^2 - 4x^3y(dy)/(dx) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/rhmj6upqrm7tvdxn9lqx4rm8dfnjpant24.png)
![\[10x(y^2 + xy(dy)/(dx)) - 2x^2y(3y + x(dy)/(dx)) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/9yg3cfy5lyszr0z0u4tlh9z4wps4kwm389.png)
![\[10x(y^2 + xy(dy)/(dx)) - 6x^2y^2 - 2x^2y(dy)/(dx) = 0\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/jis1v1ygqndigcqzudt81r7e3x714jb5z4.png)
![\[10x(y^2 + xy(dy)/(dx)) = 6x^2y^2 + 2x^2y(dy)/(dx)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/mo2eumxm02jt18gpd534mk0hwb9slq8i7m.png)
![\[10xy^2 + 10x^2y(dy)/(dx) = 6x^2y^2 + 2x^2y(dy)/(dx)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/qyfk1h64cmfusvo2j8x4eoemzz1lm0pbwu.png)
![\[10x^2y(dy)/(dx) - 2x^2y(dy)/(dx) = 6x^2y^2 - 10xy^2\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/ec356k9tse2147htco6spejfpkmj9b9r5w.png)
![\[8x^2y(dy)/(dx) = 2x^2(3y^2 - 5y)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/mmqypc1nazuzn4qyhb5r0bvyjcmb2vh3qc.png)
Now, we'll show that
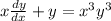 holds using the relationship
holds using the relationship
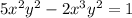 :
:
![\[x(dy)/(dx) + y = (1 + 2x^3y^2)/(y) = (1 + 2x^3y^2)/((1)/(5x^2) + 2x^3) = x^3y^3\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/mathematics/high-school/v4axfzrqzn24nubt1e8kybpdsrzrm13l1i.png)
Therefore, the implicit solution
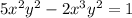 is indeed a solution of the differential equation
is indeed a solution of the differential equation
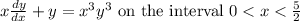 .
.
Question:
(a) Show that
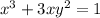 is an implicit solution of the differential equation
is an implicit solution of the differential equation
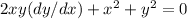 on the interval
on the interval
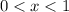 .
.
(b) Show that
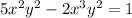 is an implicit solution of the differential equation
is an implicit solution of the differential equation
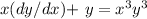 on the interval
on the interval
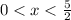 .
.