To find the pOH of a 0.35 mol/L
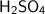 solution, we need to determine the hydroxide ion concentration (
solution, we need to determine the hydroxide ion concentration (
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/3aiaij67fqxuq1xm0jwjput5ngrrnwsh58.png) ) and then calculate the pOH.
) and then calculate the pOH.
Since
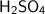 is a strong acid, it completely dissociates in water. It produces two moles of H+ ions for every mole of
is a strong acid, it completely dissociates in water. It produces two moles of H+ ions for every mole of
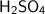 . Therefore, the concentration of H+ ions is also 0.35 mol/L.
. Therefore, the concentration of H+ ions is also 0.35 mol/L.
In a neutral solution, the concentration of
 ions is equal to the concentration of H+ ions, which is 0.35 mol/L in this case.
ions is equal to the concentration of H+ ions, which is 0.35 mol/L in this case.
To calculate pOH, we can use the formula:
![\displaystyle\sf pOH=-\log_(10) [OH^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/wuh50dcbb4v1g7mt8w39bwbb76maxn2ao1.png)
Substituting the value of
![\displaystyle\sf [OH^(-)]=0.35](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/o2k1lwkpbkkcbztuh5psjpzrkl8a80dmk7.png) , we have:
, we have:
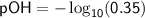
Calculating this using a calculator or logarithmic table, we find that the pOH of the 0.35 mol/L
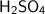 solution is approximately 0.46.
solution is approximately 0.46.
Therefore, the pOH of the given solution is 0.46.