Answer: The amount of energy required is 1066 kJ.
Step-by-step explanation:
Our 377 g of liquid water will pass through three distinct stages as it heats:
- Stage 1: Heating liquid water from 0°C to 100°C (the boiling point of water).
- Stage 2: Vaporizing the liquid water at 100°C into steam at 100°C.
- Stage 3: Heating steam from 100°C to 172°C.
We must track the energy required over each stage separately.
Stage 1:
We have 377 g of liquid water at 0°C and will heat it to 100°C to reach boiling point. We know that the specific heat for water is 4.184 J/g · °C.
Using the heat equation,
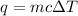 , we have:
, we have:
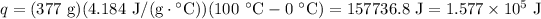
Stage 2:
We must vaporize the liquid water at 100°C into steam at 100°C. We know that the molar heat of vaporization of water is 40.79 kJ/mol.
377 g H2O x 1 mol H2O / (18.016 g H2O) x 40.79 kJ / mol = 853.6 kJ
Stage 3:
Now, we must finish the task by heating steam from 100°C to 172°C. We know that the specific heat for steam is 1.99 J/g · °C.
Using the heat equation,
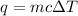 , we have:
, we have:
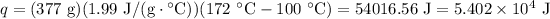
Conclusion:
We now calculate the total amount of energy in kJ. We must convert our Stage 1 and Stage 3 calculations into kJ first. Then,
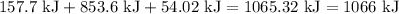
after accounting for significant digits.