When the temperature changes to 20.0 K and the pressure changes to 380 kPa, the new volume will be approximately 0.2 L (200.0 mL).
To solve this problem using the gas laws, we need to use the Ideal Gas Law. This law states that the product of the pressure and the volume of a gas is proportional to the absolute temperature.
The equation of the Ideal Gas Law is the following:
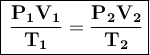
Where:
- P₁ = initial pressure = 760 kPa
- V₁ = initial volume = 50.0 mL = 0.050 L
- T₁ = initial temperature = 10.0 K
- P₂ = Final pressure = 380 kPa
- T₂ = final temperature = 20.0 K
- V₂ = Final volume = ?
We clear for V₂:

Where:
- P₁ = initial pressure
- V₁ = initial volume
- T₁ = initial temperature
- P₂ = Final pressure
- T₂ = final temperature
- V₂ = Final volume
Substituting the known values:



When the temperature changes to 20.0 K and the pressure changes to 380 kPa, the new volume will be approximately 0.2 L (200.0 mL).