Final Answer:
The centroidal axis (y) for the cross-sectional area of the T-beam is located at
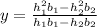 , where
, where
 and
and
 are the height and width of the upper flange, and
are the height and width of the upper flange, and
 and
and
 are the height and width of the stem. The moments of inertia
are the height and width of the stem. The moments of inertia
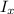 and
and
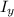 are calculated based on the centroidal axis.
are calculated based on the centroidal axis.
Step-by-step explanation:
In the given T-beam, the centroidal axis (y) is determined using the formula
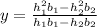 , where
, where
 and
and
 are the dimensions of the upper flange, and
are the dimensions of the upper flange, and
 and
and
 are the dimensions of the stem. This formula represents the centroidal axis as the weighted average of the individual centroids of the flange and the stem, considering their respective dimensions.
are the dimensions of the stem. This formula represents the centroidal axis as the weighted average of the individual centroids of the flange and the stem, considering their respective dimensions.
To calculate the moments of inertia
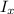 and
and
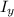 , the parallel axis theorem is often applied. The formula for
, the parallel axis theorem is often applied. The formula for
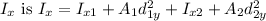 , where
, where
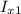 and
and
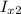 are the moments of inertia of the flange and the stem about their own centroidal axes, and
are the moments of inertia of the flange and the stem about their own centroidal axes, and
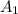 and
and
 are their respective areas. The distances
are their respective areas. The distances
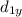 and
and
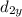 are the distances between their centroidal axes and the overall centroidal axis (y). A similar formula is used for
are the distances between their centroidal axes and the overall centroidal axis (y). A similar formula is used for
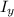 , considering the distances along the x-axis.
, considering the distances along the x-axis.
In summary, the centroidal axis and moments of inertia are crucial parameters in structural engineering, influencing the beam's behavior under different loading conditions. These calculations help engineers design and analyze T-beams for optimal performance and safety.