The final partial pressures of
 and
and
 are 316.67 torr and 50.67 torr, respectively, and the total pressure is 367.33 torr.
are 316.67 torr and 50.67 torr, respectively, and the total pressure is 367.33 torr.
The final partial pressures of
 and
and
 after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened can be calculated using the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its volume.
after the stopcock between the two flasks is opened can be calculated using the ideal gas law, which states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its volume.
Given that the initial volume of
 is 2.00 L and its initial pressure is 475 torr, when the volume increases to 3.00 L, the final pressure of
is 2.00 L and its initial pressure is 475 torr, when the volume increases to 3.00 L, the final pressure of
 (
(
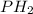 ) can be calculated as follows:
) can be calculated as follows:
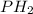 = (Initial Pressure of
= (Initial Pressure of
 * Initial Volume of
* Initial Volume of
 ) / Final Volume
) / Final Volume
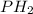 = (475 torr * 2.00 L) / 3.00 L
= (475 torr * 2.00 L) / 3.00 L
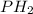 ≈ 316.67 torr
≈ 316.67 torr
Similarly, the initial volume of
 is 1.00 L and its initial pressure is 0.200 atm. Converting this pressure to torr (since 1 atm = 760 torr), we get an initial pressure of 152 torr for
is 1.00 L and its initial pressure is 0.200 atm. Converting this pressure to torr (since 1 atm = 760 torr), we get an initial pressure of 152 torr for
 . When the volume increases to 3.00 L, the final pressure of
. When the volume increases to 3.00 L, the final pressure of
 (P
(P
 ) can be calculated as follows:
) can be calculated as follows:
P
 = (Initial Pressure of
= (Initial Pressure of
 * Initial Volume of
* Initial Volume of
 ) / Final Volume P
) / Final Volume P

= (152 torr * 1.00 L) / 3.00 L
P
 ≈ 50.67 torr
≈ 50.67 torr
The total pressure in the system after the stopcock is opened is the sum of the partial pressures of
 and
and
 :
:
Total Pressure =
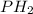 +
+
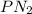
Total Pressure = 316.67 torr + 50.67 torr
Total Pressure ≈ 367.33 torr
So, the final partial pressures of
 and
and
 are approximately 316.67 torr and 50.67 torr, respectively, and the total pressure is approximately 367.33 torr
are approximately 316.67 torr and 50.67 torr, respectively, and the total pressure is approximately 367.33 torr