Explanation:
Example 1:
Given pair: (3;2)
{2x + 3y = 12,
{x - 4y = -5;
Make x the subject from the 2nd equation:
x = -5 + 4y
Replace x in the 1st equation:
2 × (-5 + 4y) + 3y = 12
-10 + 8y + 3y = 12
11 y = 12 + 10
11y = 22 / : 11
y = 2
y = 2x = -5 + 4 × 2 = -5 + 8 = 3
The answer: (3;2)
The given pair is the solution of the system of equations
.
Example 2:
Given pair: (0; -4)
{x + y = -4,
{x - 5y = 20;
x = -4 - y
(-4 - y) - 5y = 20
-4 - y - 5y = 20
-6y = 20 + 4
-6y = 24 / : (-6)
y = -4
y = -4x = -4 - (-4) = -4 + 4 = 0
The answer: (0; -4)
The given pair is the solution
.
Example 3:
Given pair: (3;3)
{x + 2y = 9,
{4x - y = 15;
x = 9 - 2y
4(9 - 2y) - y = 15
36 - 8y - y = 15
-9y = 15 - 36
-9y = -21 / : (-9)
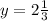
The given pair is not the solution
.
Example 4:
Given pair: (1; -2)
{2x - 3y = 8,
{3x + 2y = -1;
2x = 8 + 3y / : 2
x = 4 + 1,5y
3(4+1,5y) + 2y = -1
12 + 4,5y + 2y = -1
6,5y = -1 - 12
6,5y = -13 / : 6,5
y = -2
y = -2x = 4 + 1,5 × (-2) = 4 - 3 = 1
The given pair is the solution
.
Example 5:
Given pair: (1;5)
{5x - 2y = -5,
{3x - 7y = -32;
-2y = -5 - 5x / : (-2)
y = 2,5 + 2,5x
3x - 7(2,5 + 2,5x) = -32
3x - 17,5 - 17,5x = -32
-14,5x = -32 + 17,5
-14,5x = -14,5 / : (-14,5)
x = 1
x = 1y = 2,5 + 2,5 × 1 = 5
The given pair is the solution
.
Example 6:
Given pair: (-1; -3)
{3x + y = -6,
{2x = 1 + y;
y = -6 - 3x
2x = 1 + (-6 - 3x)
2x = 1 - 6 - 3x
2x + 3x = 1 - 6
5x = -5 / : 5
x = -1
x = -1y = -6 - 3 × (-1) = -6 + 3 = -3
The given pair is the solution