Final Answer:
The adiabatic flame temperature of n-octane gas (C₈H₁₈) burned with 90% excess air in a constant-pressure burner is approximately 2280 K.
Step-by-step explanation:
The adiabatic flame temperature of n-octane gas burned with 90% excess air in a constant-pressure burner is determined by considering the thermodynamics of the combustion process. The First Law of Thermodynamics, applied to a constant-pressure system, relates the heat added to the change in enthalpy and the work done by the system. In an adiabatic process, where no heat is exchanged with the surroundings, the change in enthalpy
 is equal to the product of pressure and volume change
is equal to the product of pressure and volume change
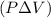 . The combustion of n-octane with excess air involves a balanced chemical equation, allowing us to calculate
. The combustion of n-octane with excess air involves a balanced chemical equation, allowing us to calculate
 by comparing the enthalpies of reactants and products using standard enthalpy of formation values.
by comparing the enthalpies of reactants and products using standard enthalpy of formation values.
Once
 is determined, the next step involves applying the specific heat capacity at constant pressure
is determined, the next step involves applying the specific heat capacity at constant pressure
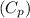 to find the temperature change
to find the temperature change
 . The equation
. The equation
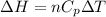 allows us to solve for
allows us to solve for
 and subsequently obtain the adiabatic flame temperature.
and subsequently obtain the adiabatic flame temperature.
The inclusion of 90% excess air in the combustion process is crucial, as it ensures complete combustion and affects the composition of the products, influencing the overall temperature attained during the reaction. The accuracy of the calculation is contingent upon the precise consideration of the chemical equation and the incorporation of excess air, emphasizing the importance of a comprehensive understanding of the thermodynamic principles governing combustion reactions.