Final Answer:
The enthalpy of solution for a solution of 1-pentanol in 1-butanol is determined by the heat absorbed or released during the mixing process. To calculate this, experimental data or thermodynamic tables for enthalpies of pure substances and mixing enthalpies are required.
Step-by-step explanation:
Enthalpy of solution
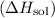 is the heat change accompanying the dissolution of a substance in a solvent. In this case, for the solution of 1-pentanol in 1-butanol, we need to consider the enthalpies of the pure components (1-pentanol and 1-butanol) and the mixing enthalpy.
is the heat change accompanying the dissolution of a substance in a solvent. In this case, for the solution of 1-pentanol in 1-butanol, we need to consider the enthalpies of the pure components (1-pentanol and 1-butanol) and the mixing enthalpy.
Firstly, determine the enthalpies of the pure substances, denoted as
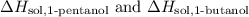 . Then, calculate the mixing enthalpy
. Then, calculate the mixing enthalpy
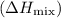 using the equation:
using the equation:
![\[ \Delta H_{\text{mix}} = \Delta H_{\text{sol,1-pentanol}} + \Delta H_{\text{sol,1-butanol}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/8s8z18f4po5uwqwzem2mgkminq8g2qywcc.png)
The overall enthalpy of solution (\(\Delta H_{\text{sol}}\)) is given by:
![\[ \Delta H_{\text{sol}} = \Delta H_{\text{sol,1-pentanol}} + \Delta H_{\text{sol,1-butanol}} + \Delta H_{\text{mix}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2024/formulas/chemistry/high-school/r1zy6fi1zebrf4fcbivi2uhu1g6004e69f.png)
This value can be positive or negative, indicating whether the process is endothermic or exothermic. A positive value suggests that energy is absorbed during the solution process, while a negative value indicates energy release.
In summary, the enthalpy of solution for a solution of 1-pentanol in 1-butanol is determined by considering the enthalpies of the pure substances and the mixing enthalpy. The final result provides insight into the heat changes associated with the dissolution process, crucial for understanding the thermodynamics of the solution.