Answer:
- the volume of the second tank is 1.77 m³
- the final equilibrium pressure of air is 221.88 kPa ≈ 222 kPa
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that;
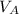 = 1 m³
= 1 m³
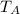 = 10°C = 283 K
= 10°C = 283 K
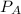 = 350 kPa
= 350 kPa
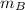 = 3 kg
= 3 kg
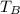 = 35°C = 308 K
= 35°C = 308 K
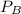 = 150 kPa
= 150 kPa
Now, lets apply the ideal gas equation;
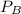
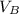 =
=
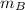 R
R
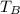
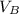 =
=
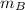 R
R
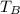 /
/
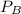
The gas constant of air R = 0.287 kPa⋅m³/kg⋅K
we substitute
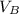 = ( 3 × 0.287 × 308) / 150
= ( 3 × 0.287 × 308) / 150
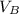 = 265.188 / 150
= 265.188 / 150
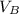 = 1.77 m³
= 1.77 m³
Therefore, the volume of the second tank is 1.77 m³
Also,
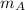 =
=
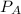
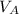 / R
/ R
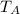 = (350 × 1)/(0.287 × 283) = 350 / 81.221
= (350 × 1)/(0.287 × 283) = 350 / 81.221
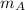 = 4.309 kg
= 4.309 kg
Total mass,
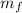 =
=
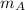 +
+
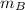 = 4.309 + 3 = 7.309 kg
= 4.309 + 3 = 7.309 kg
Total volume
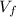 =
=
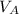 +
+
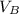 = 1 + 1.77 = 2.77 m³
= 1 + 1.77 = 2.77 m³
Now, from ideal gas equation;
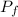 =
=
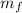 R
R
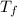 /
/
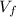
given that; final temperature
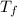 = 20°C = 293 K
= 20°C = 293 K
we substitute
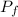 = ( 7.309 × 0.287 × 293) / 2.77
= ( 7.309 × 0.287 × 293) / 2.77
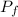 = 614.6211119 / 2.77
= 614.6211119 / 2.77
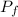 = 221.88 kPa ≈ 222 kPa
= 221.88 kPa ≈ 222 kPa
Therefore, the final equilibrium pressure of air is 221.88 kPa ≈ 222 kPa