Answer:
x = 4.03 10⁻² m
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's start by finding the acceleration for each particle due to the electric field
F = ma
the electric force is F = qE
q E = m a
a = qE / m
proton
m = 1.67 10⁻²⁷ kg
a₁ = 1.6 10⁻¹⁹ 698 /1.67 10⁻²⁷
a₁ = 6.687 10¹⁰ m / s²
directed to the right
electron
m = 9.11 10⁻³¹ kg
a₂ = 1.6 10⁻¹⁹ 698 /9.11 10⁻³¹
a₂ = 1.23 10¹⁴ m / s²
directed to the left
Taking the acceleration of the two bodies, we set a reference system with zero at the initial position of the proton on the positive plate, the point where it is located is x for the proton and x for the electron,
for the proton
x₁ = x₀₁ + v₀₁ t + ½ a₁ t²
as we start from rest vo1 = 0 and the initial position is xo = 0
x₁ = ½ a₁ t²
for the electron
x₂ = x₀₂ + v₀₂ t + ½ a₂ t²
in this case the initial velocity is zero v₀₂ = 0 and the initial position is x₀₂=d
x₂ = x₀₂ + ½ a₂ t²
at the meeting point x₁ = x₂, so we can equalize the two equations
½ a₁ t² = x₀₂ + ½ a₂ t²
½ t² (a₁ -a₂) = x₀₂
t =
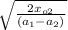
let's calculate
t =
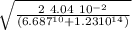
t =

t = 2.56 10⁻⁸ s
now we can calculate the position
x = ½ a₂ t²
x = ½ 1.23 10¹⁴ (2.56 10⁻⁸)²
x = 4.03 10⁻² m