Answer:
Position of equilibrium changes with increase in pressure but equilibrium constant remains same
Step-by-step explanation:
For a reaction -
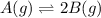 , equilibrium shifts toward left with increase in pressure.
, equilibrium shifts toward left with increase in pressure.
Because, number of gas molecules increases in forward direction which means pressure increases in forward direction. According to Le-chatlier principle, equilibrium will shift toward backward direction or towards left to minimize the increased pressure as well as keep the equilibrium constant same.
For a reaction-
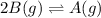 , equilibrium shifts toward right with increase in pressure.
, equilibrium shifts toward right with increase in pressure.
Explanation for this is same as above.